...
| Dive | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
|
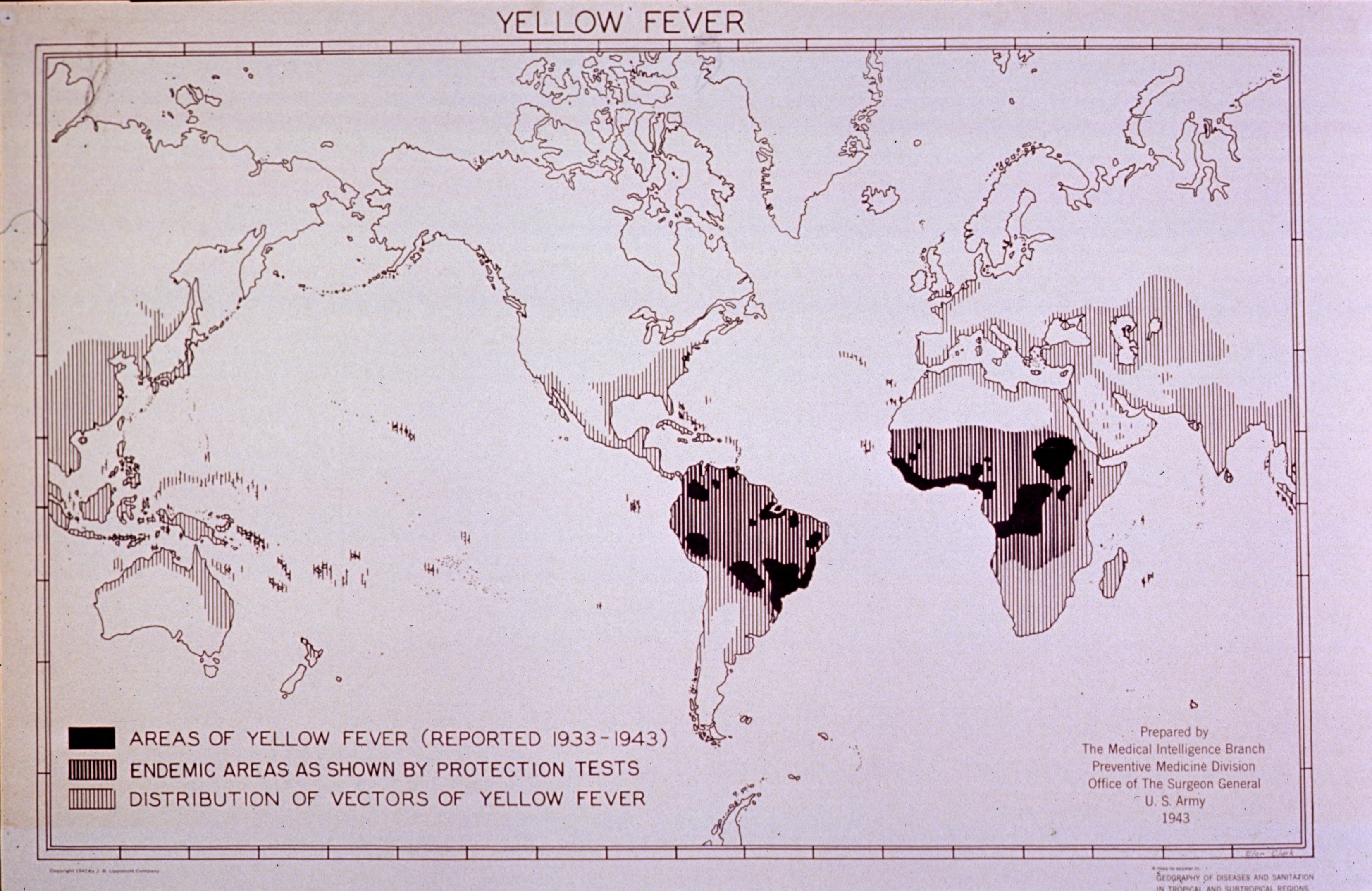
World War II created a huge demand for the yellow fever vaccine. The United States used the Rockefeller Institute vaccine for almost 7 million doses. Later some 26,000 cases of jaundice were recorded and mortality rates of 3 per 1000 (but it was later shown to be Hep. B). An investigation ensued. The serum seemed to be the culprit. The serum was donated by medical professionals, students, etc. at Johns Hopkins who when later tested, it was revealed that several of the donors had a history of jaundice.
The yellow fever vaccine was first licensed in 1938. From 1943 until her retirement in 1971, Dr. Margaret Pittman worked to assess the efficacy of and establish national and international standards for the production of the yellow fever vaccine
...
| class | grid-col-6 |
|---|
...
| class | caption |
|---|
...
.
...
| class | credit |
|---|
...
After WWII, the French and 17D vaccines widely used. By 1982 the French vaccine was discontinued. Since 1982, developments have included greater stabilization of the vaccine, with a longer storage life. In 1985, the complete genome of the yellow fever virus was published, allowing new research. Today all the vaccines are derived from two sub-strains of 17D.
...